2D rogue game
This project was developed as part of the CPT204 Object-Oriented Programming course, focusing on implementing advanced graph algorithms to create intelligent behaviors in a simplified version of the classic 2D game Rogue. The game involves navigating a dungeon, collecting items, and avoiding enemies, with both the player (Rogue) and the enemy (Monster) employing strategic movement. The project highlights the use of pathfinding and cycle detection algorithms to simulate effective pursuit and evasion dynamics.
AI Behavior Demonstration
The following GIFs showcase the dynamic interaction between the Monster and the Rogue, highlighting the effectiveness of the algorithms implemented in this project. Each scenario demonstrates the decision-making process of both agents and the resulting outcomes based on the dungeon layout and available strategies:
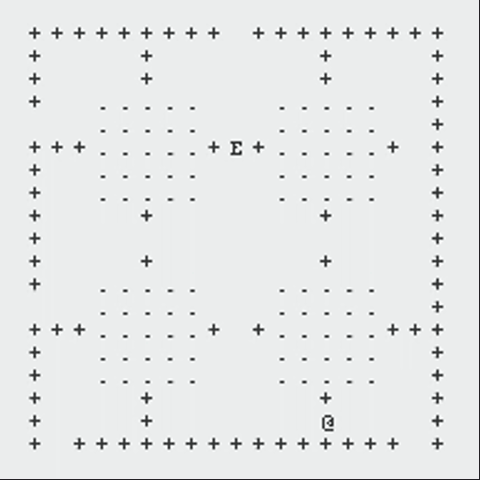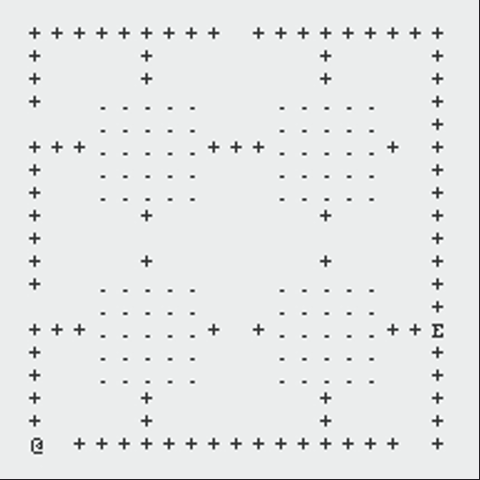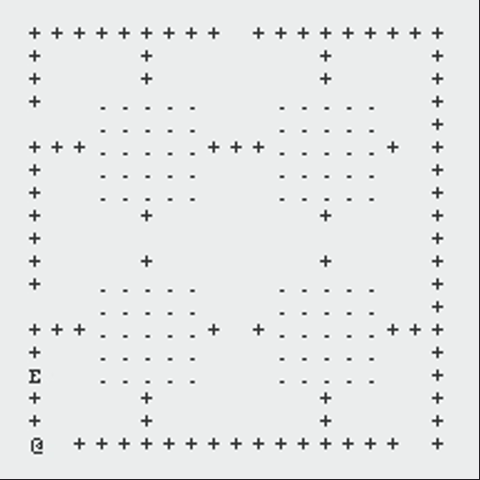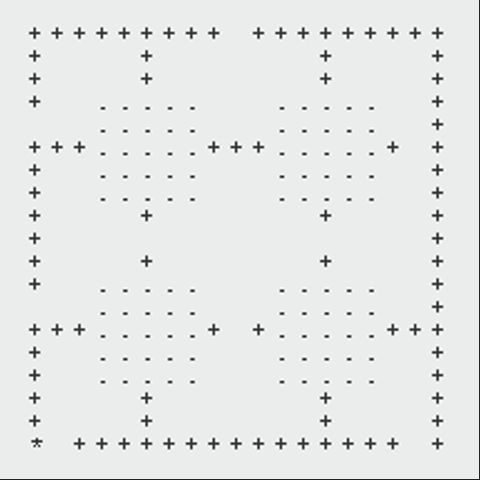
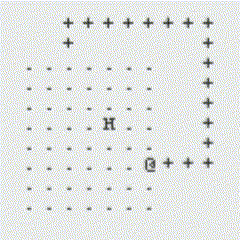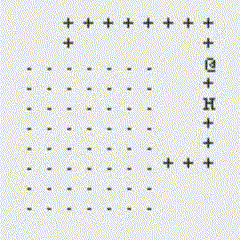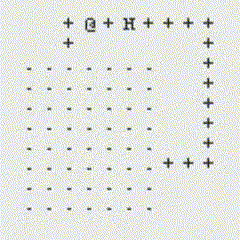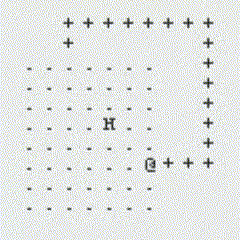
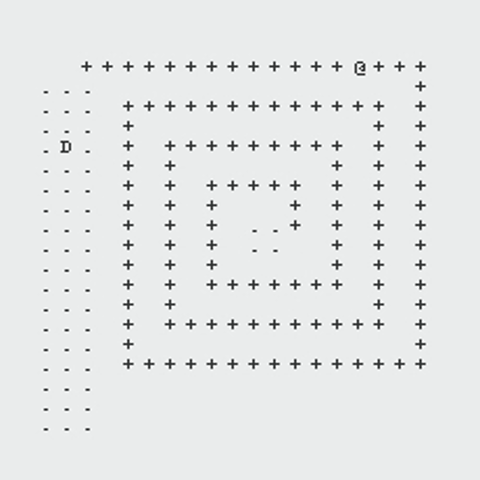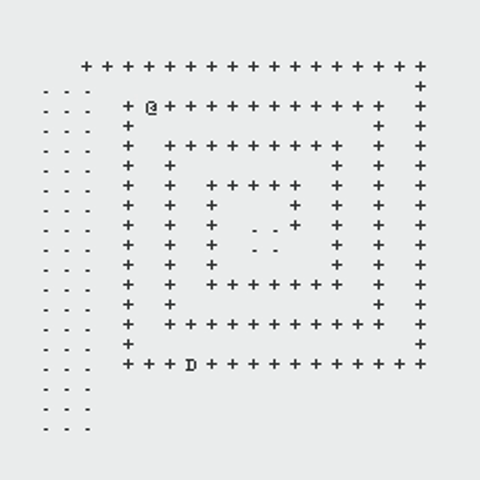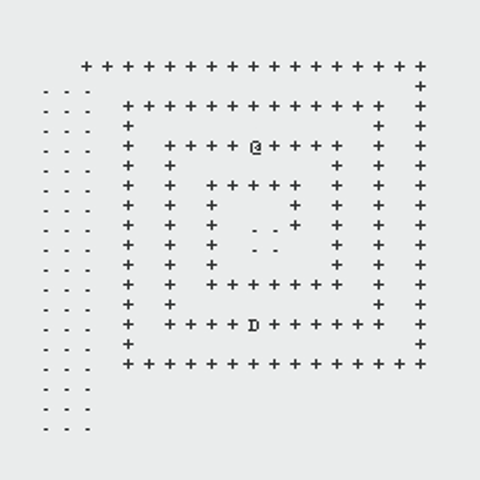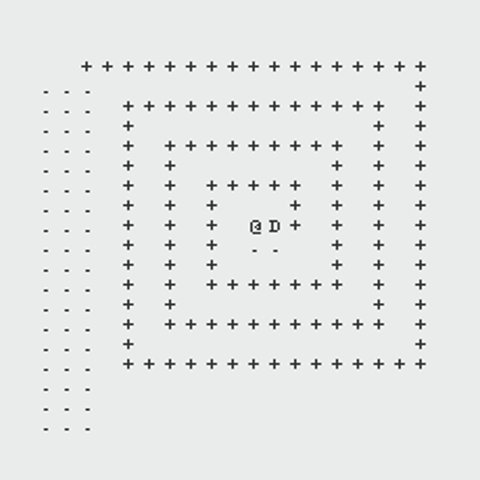
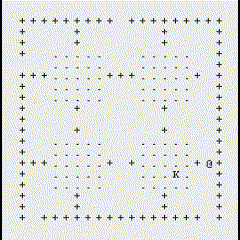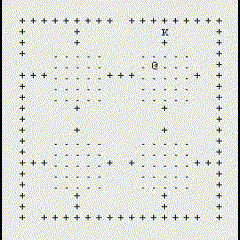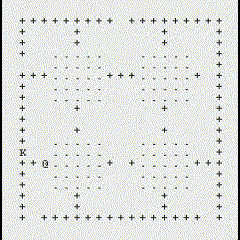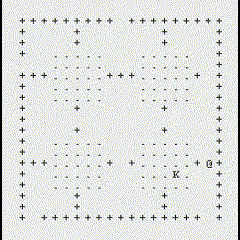
Path Finding Algorithm
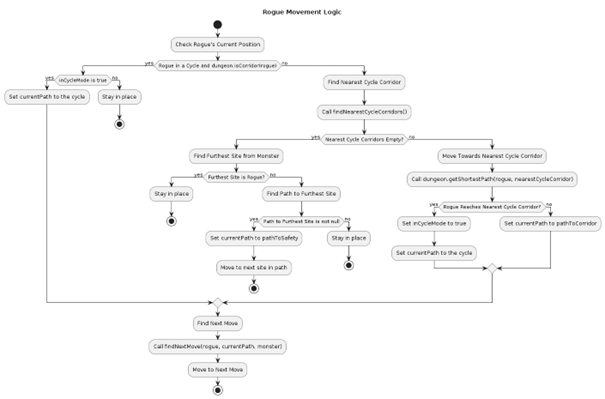
Since the most important part of the game is the path finding algorithm, I will introduce the algorithm in detail.
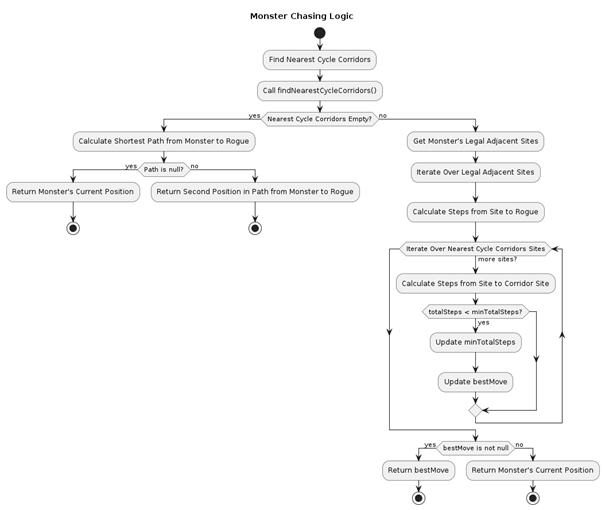
Monster Algorithm: Pursuit Strategies
The Monster’s behavior centers around intelligently tracking and intercepting the Rogue using graph-based strategies:
-
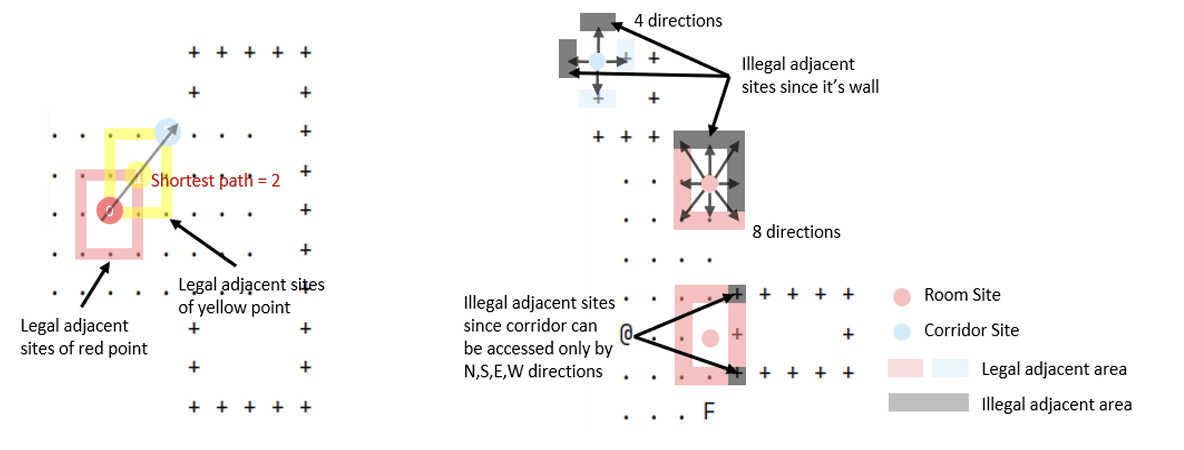
Pathfinding with BFS:
The Monster uses a Breadth-First Search (BFS) algorithm to calculate the shortest path to the Rogue. This ensures dynamic, layer-by-layer exploration of the dungeon for optimal pursuit. -
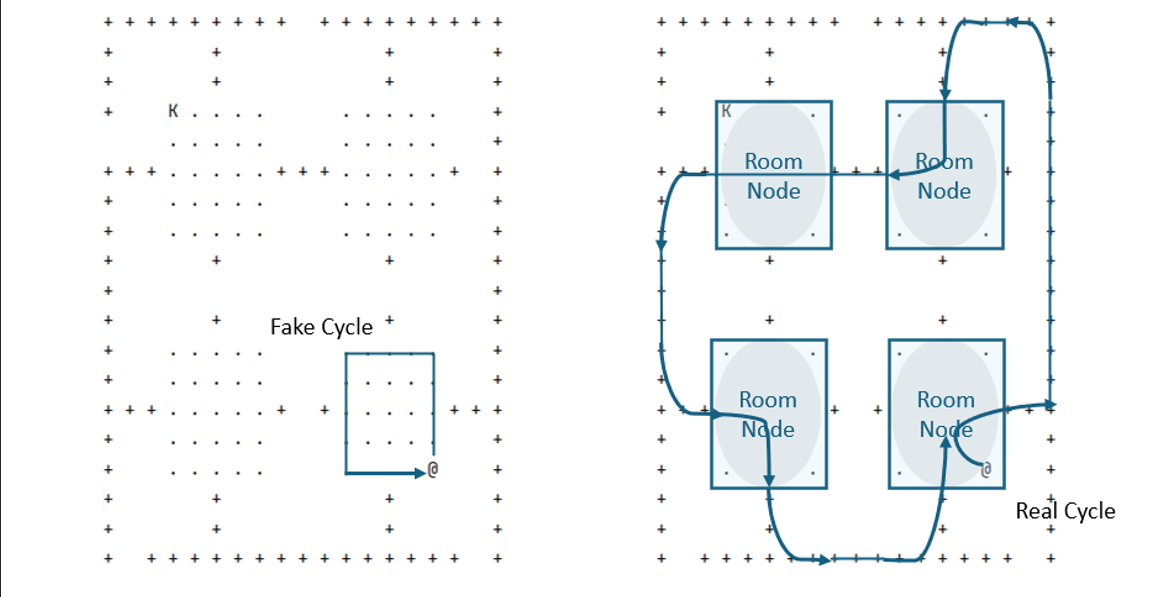
Cycle Detection with DFS:
The algorithm identifies closed-loop structures (cycles) in the dungeon using Depth-First Search (DFS). These cycles are critical for understanding potential Rogue escape routes. Room areas are abstracted into single nodes to simplify detection and improve computational efficiency.
- Hunting Strategies:
- Shortest Path Pursuit: The Monster directly follows the shortest path to the Rogue.
- Early Interception: If the Rogue attempts to enter a cycle, the Monster prioritizes blocking the cycle’s entry point, using a heuristic to choose the move that minimizes its distance to both the Rogue and the cycle entry. This strategy disrupts the Rogue’s chances of using cycles to evade capture.
Rogue Algorithm: Evasion Strategies
The Rogue employs adaptive strategies based on the dungeon layout and the Monster’s actions to ensure survival or prolong evasion:
-
Cycle-Based Strategy (Winning Scenarios):
- Cycle Identification & Usage: The Rogue identifies reachable cycles in the dungeon where it can evade the Monster indefinitely.
- Cycle Movement: Once inside a cycle, the Rogue ensures it stays one step ahead of the Monster by maintaining a safe distance within the loop.
-
Pathfinding for Cycle Entry:
The Rogue calculates the shortest path to the nearest cycle entry and moves strategically to enter it when threatened. -
Survival Strategy (Losing Scenarios):
If no reachable cycle exists, the Rogue chooses a destination as far from the Monster as possible, maximizing survival time. -
Dynamic Adaptation:
The Rogue’s algorithm continuously evaluates the game state, switching between cycle-based and survival strategies to optimize its moves.